MLflow
The integration is experimental.
The integration expects that the MLflow Tracking Server has the proxied artifact storage access enabled.
Overview
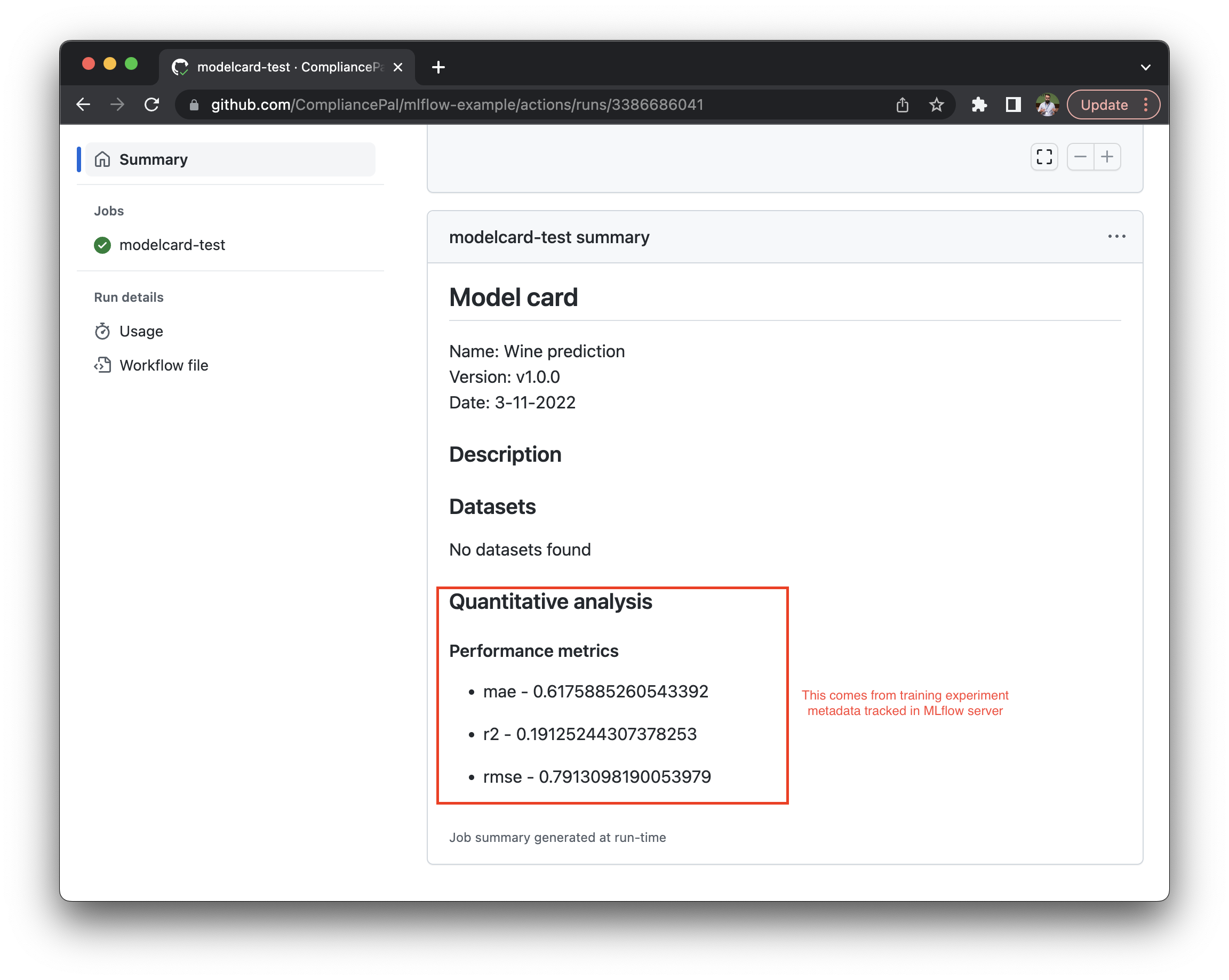
The integration takes as input the modelcard document tracked in git and augments it with with experiment information tracked by the MLflow server.
Interaction
The Data Scientist performs experiments in their development environment. The runs are tracked by the MLflow server (1-2). The winning experiment is selected by including the run_id in the model card document and making a new commit (3-4):
model_details:
...
run:
type: mflow
id: 2a84d204c6794965bc36641b46b77255
...
GitHub triggers the modelcard-action and it receives the commit (5). The action fetches the run details from the MLflow server (6), performs validation (7), adds the augmented model card to experiment run as an artifact (8), and renders the model card.
MLflow tracking server instance
Run local test server
Using docker-compose is an effective way to start a MLflow tracking server. The example below is based on mlflow-docker-compose. The web service command starts the tracking server with the proxied artifact storage:
version: '3.7'
services:
minio:
restart: always
image: minio/minio@sha256:d28c69eda85fb4c362d2a8976274da8f369398fc943b0c238c50722fd0c578c4
container_name: mlflow_s3
ports:
- '9000:9000'
- '9001:9001'
command: server /data --console-address ':9001' --address ':9000'
environment:
- MINIO_ROOT_USER=${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
- MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD=${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}
volumes:
- .cache/minio_data:/data
mc:
image: minio/mc@sha256:d281c2bfce56c727dc229643f8df99e24295fae586aaf6acb859eb2dd4c66ca4
depends_on:
- minio
container_name: mc
env_file:
- .env
entrypoint: >
/bin/sh -c "
/tmp/wait-for-it.sh minio:9000 &&
/usr/bin/mc alias set minio http://minio:9000 ${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID} ${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} &&
/usr/bin/mc mb minio/mlflow;
exit 0;
"
volumes:
- ./wait-for-it.sh:/tmp/wait-for-it.sh
db:
restart: always
image: mysql/mysql-server@sha256:fcbe88694872e88ae406bc69540211505eae922a182690d85be6af1a48e5ca0a
container_name: mlflow_db
ports:
- '3306:3306'
environment:
- MYSQL_DATABASE=${MYSQL_DATABASE}
- MYSQL_USER=${MYSQL_USER}
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=${MYSQL_PASSWORD}
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=${MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- .cache/dbdata:/var/lib/mysql
web:
restart: always
build: ./mlflow
image: mlflow_server
container_name: mlflow_server
depends_on:
- mc
- db
ports:
- '5000:5000'
environment:
- MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL=http://minio:9000
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}
# start the tracking server with proxied artifact storage
command: >
mlflow server
--backend-store-uri mysql+pymysql://${MYSQL_USER}:${MYSQL_PASSWORD}@db:3306/${MYSQL_DATABASE}
--artifacts-destination s3://mlflow/mlartifacts
--serve-artifacts
--host 0.0.0.0
The local test server can be exposed with ngrok, adding basic authentication:
ngrok 5000 --bind-tls true --auth user:password
The public url where the tracking server is available follows this format https://{your-instance}.ngrok.io.
MLflow project configuration
The MLflow project needs to be developed in a Git repository stored on GitHub.
Configure secrets
Add the MLflow tracking server as a GitHub secret:
MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI=https://user:password@{your-instance}.ngrok.io
Create workflow
Add the following workflow to your GitHub repository. The integration with the MLflow tracking server is enabled by the MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI environment variable.
name: modelcard-test
on:
pull_request:
branches: [main]
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
mlflow-modelcard:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout branch
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Check for model card file
uses: CompliancePal/modelcard-action@mlflow-action-experiments
env:
MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI: ${{ secrets.MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI }}
with:
modelcard: modelcard.yaml
Enhancing the experiment run artifacts
The modelcard-action adds the modelcard metadata document (e.g. modelcard.json) to the artifacts created during the tracked experiment run.
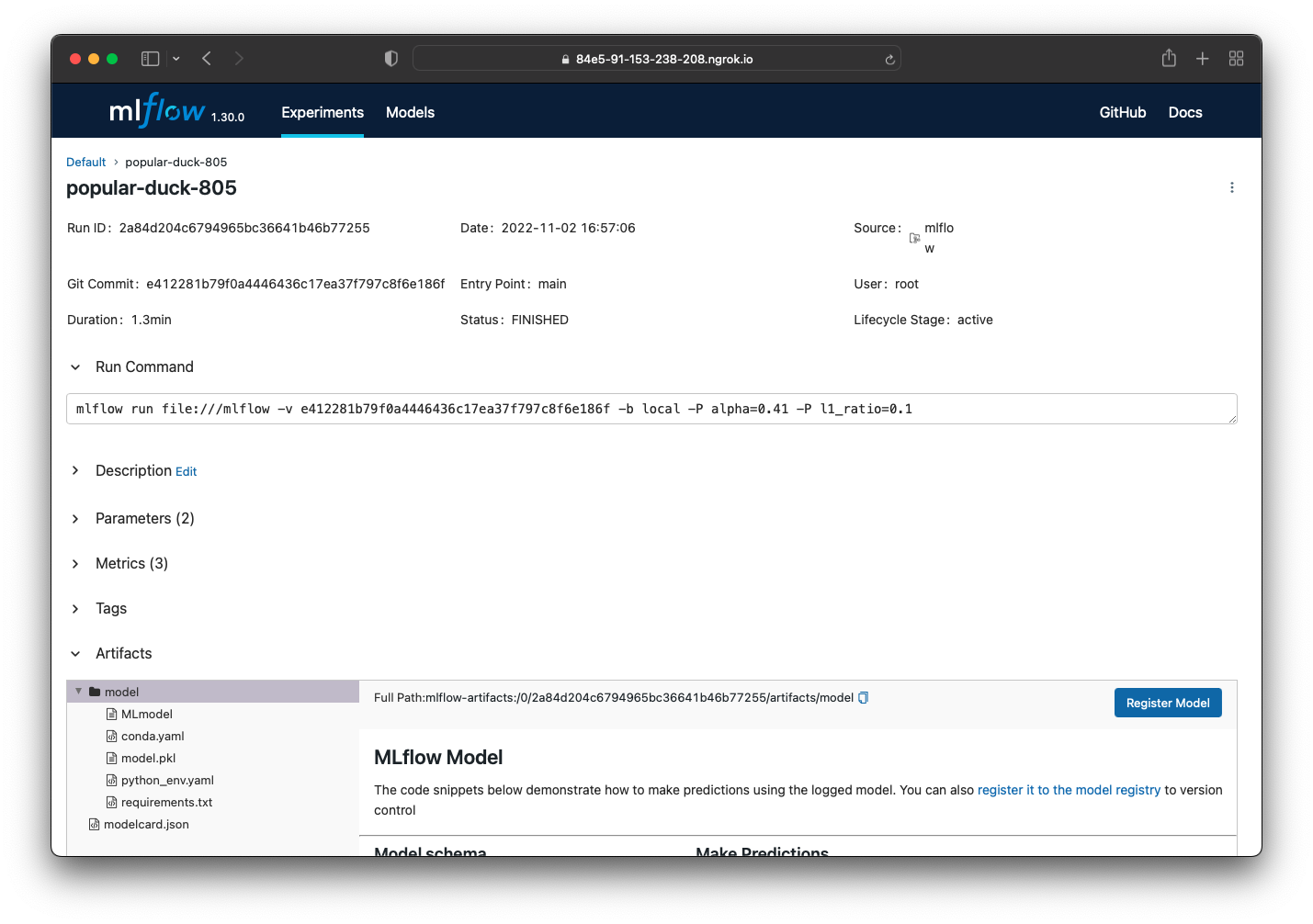
Example
An example usage of the integration is available at mlflow-example.